SDA SHS Economics Mock Questions
SDA SHS economics mock questions
SDA SHS Economics Mock Questions
Very experienced tutors at designed these SDA SHS economics mock questions. The questions enable candidates to pass their examination very well.
See also: PARKOSO SHS economics mock questions
Paper 1: Objectives
SDA SHS economics mock questions Answer all questions in this section
1. Many buyers and sellers trading in homogeneous products are all features of a:
A. Capitalist economy
B. Perfect market
C. Planned market
D. Command market
2. When two commodities are supplied from one source, they are in:
A. Competitive supply
B. . Joint supply
C. Derived supply
D. Effective supply
3. A consumer is in equilibrium when:
A. His market supply is equal to his market demand
B. The market is also in equilibrium
C. He maximize his satisfaction from spending his income
D. He has consumed all he wants
4. Explain Five(5) reasons why government control prices.
A. Mixed economy
B. Socialist economy
C. Capitalist economy
D. black economy
5. In a market economy the decision as to what is be to produced depends on the:
A. Entrepreneur
B. Government
C. Banks
D. Consumer
SDA SHS economics mock questions
The age distribution of a country’s population is shown below. Use the information to answer questions 6 and 7
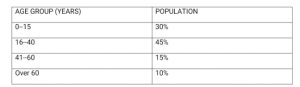
6. What is the percentage of the working population
A. 75% B. 45% C. 60% D. 15
7. What is the dependency ratio?
A. 1:2 B.3:2 C:2:3 D.6:1
8. The size of a country's population cannot be influenced by the:
A. Rural-urban migration
B. Number of births
C. Death rate
D. Fertility rate
9. If the available resources of a country cannot sustain it's population ,then there is:
A. Declining population
B. Under population
C. Over population
D. increasing population
10. The branch of Economics that focuses on individual behavior is known as:
A. Marcroeconomics
B. Positive economics
C. Microeconomics
D. Normative economics
SDA SHS economics mock questions
11. A table as a tool of economic analysis is:
A. A symbolic presentation of facts
B. A systematically arranged set of figures on rows and columns
C. An instrument with four legs on which one can write
D. A pictorial representation of ideas
12. The production possibility curve will shift rightward when there is:
A. Inflation
B. Inflation
C. Acquisition
D. Deflation
13. Full employment in the economy
E. A point outside the production possibilities curve indicates that:
A. Production is attainable
B. Production is not attainable
C. Some resources have not been provided
D. Resources have not been effectively combined
14. Adam Smith defined economics as an inquiry into the nature and causes of wealth of nations. To him economics is concerned with:
A. Resource allocation
B. Nature of business
C. Wealth making
D. Science of economics
15. Which of these is not usually the function of a wholesaler?
A. Transportation
B. Advertising
C. Storage
D. After -sale-service
SDA SHS economics mock questions
16. By-passing the middleman in the chain of distribution can lead to:
A. An increase in government tax revenue\
B. The creation of artificial scarcity
C. High prices of goods and services
D. A problem of unemployment of labour
17. Hoarding is a problem associated with:
A. Production
B. Barter system
C. Distribution
D. Consumption
18. Scale of preference refers:
A. Increasing the size of a firm
B. Arrangement of needs in order of priority
C. Increasing utility as more goods are consumed
D. The alternative forgone as choice is made
19. "I cannot go to the training with you because I have an assignment; says Rukaya to Waki Rukaya’s statement refers to the issue of:
A. scarcity of resources
B. Scale of preference
C. Opportunity cost
D. Choice of two goods
20. Household as an economic unit, aims at maximizing:
A. Consumption
B. Satisfaction
C. Profit
D. Production
SDA SHS economics mock questions
21. John opted to watch soccer every Sunday afternoon rather than read in the library. According to John, reading is:
A. Explicit cost
B. Implicit cost
C. Real cost
D. Economic cost
22. Patents are examples of:
A. Natural barriers if entry
B. Illegal barriers of entry
C. Legal barriers of entry
D. Natural barriers of entry
23. Which of the following is a feature of monopoly?
A. Many sellers
B. Many buyers
C. Restricted entry
D. Many buyers
E. free entry
24. In order to increase revenue, government should tax commodities for which demand is:
A. Perfectly price elastic
B. Unitary elastic
C. Price elastic
D. Price inelastic
25. Goods with positive income elasticities are called:
A. Inferior goods
B. Normal goods
C. Substitute goods
D. Complementary good
SDA SHS economics mock questions
26. When income rises, less of a good is bought. This situation describes:
A. Giffen goods B. superior good C. An inferior good An ostentation
26. Unemployment due to physical disability is referred to as:
A. cyclical unemployment
B. Residual unemployment
C. Frictional unemployment
D. Structural unemployment
27. The agricultural sector of many West African countries is characterized by:
A. Structural unemployment
B. Voluntary unemployment
C. Full employment
D. Seasonal unemployment
28. Debenture holders receive:
A. Profit B. Interest C. Dividend D. Wages
29. The main aim of establishing a public corporation is to:
A. Provide essential services
B. Maximize profits
C. Acquire more assets
D. Minimize the cost of production
30. Which of the following business organizations is likely to experience disagreements between management and shareholders?
A. Co-operative society
B. Sole trader
C. Partnership
D. Joint stock company
SDA SHS economics mock questions
31. A partner who contributes only capital to a partnership is called:
A. A working partner
B. A sleeping partner
C. An active ownership
D. Proactive
32. The last resort of trade union is dispute is:
A. Sit down action
B. Work to rule
C. Negotiations
D. Strike action
33. The labour force is made up of those who are:
A. Members of the trade unions
B. Working or searching for work
C. Over 18 years of age
D. Actively employed
34. The poorer the country, the larger percentage of the total labour force engaged in:
A. Trading
B. Construction
C. Agriculture
D. Manufacturing
35. Which of the following coefficients of elasticity indicates that demand is perfectly inelastic?
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 5
SDA SHS economics mock questions
36. If demand for a commodity is fairly elastic, a tax imposed on the commodity:
A. Will have greater impact on the seller
B. Is borne only by the consumer
C. Is borne only by the manufacturer
D. Will have greater impact on the buyer
37. A demand curve is parallel to the x-axis indicates:
A. Fairly elastic demand
B. Perfectly elastic demand
C. Perfectly inelastic demand
D. Fairly inelastic demand
38. A firm producing a product with elastic demand can increase revenue by:
A. Increasing price
B. Reducing price
C. Expanding output
D. Reducing output
39. Income elasticity of demand is likely to be negative for:
A. Gari
B. Beer
C. Meat
D. Car
40. A successfully advertising campaign will generally make the demand for the advertised product:
A. Constant
B. Fall
C. Elastic
D. Inelastic
SDA SHS economics mock questions
41. Another term for equilibrium price is:
A. Human price
B. Artificial Price
C. Natural price
D. Gold price
42. When the quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded:
A. A surplus is created
B. Producers will increase the price
C. A shortage will occur
D. Consumers will bid up the price
Use the table on demand and supply schedule of a commodity below to answer Questions 43 to
44
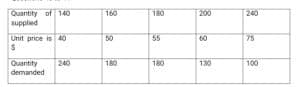
43. The equilibrium price is:
A. $50
B. $55
C. $60
D. $70
44. When the unit price is $75:
A. Quantity supplied equals quantity demanded
B. Excess demand is 100 units
C. Excess supply is 140 units
D. Quantity supplied is less than quantity demanded
45. Regulations used to prevent market prices from failing are called:
A. Minimum pricing
B. Maximum pricing
C. Rationing
D. Subsidies
SDA SHS economics mock questions
46. Raw materials form part of a firm’s:
A. Fixed cost
B. Average cost
C. Marginal cost
D. Variable cost
47. When average cost is falling , marginal cost must be:
A. Less than average
B. Rising
C. Greater than average cost
D. Failing
48. Marginal costs can be calculated from:
A. Units costs
B. Fixed costs
C. Variable costs
D. Average cost
49. Which of the following is an implicit cost of production?
A. Cost of production
B. Payment of raw materials
C. Wages paid to casual workers
D. Proprietors time
50. The accountant's cost is made up of:
A. Explicit cost only
B. Implicit cost only
C. Variable cost only
D. Fixed cost only
Paper 2: Written
SECTION B: DATA RESPONSE
SDA SHS economics mock questions: Answer Only ONE (1) question from this section
1. The table below shows the schedule of the total revenue of a farmer who produces rice.
Use the information in the table to answer the questions which follow.
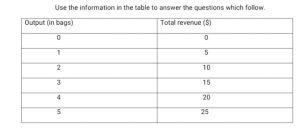
For each level of output, calculate:
A. Average revenue (AR) (5 MARKS)
B. Marginal revenue (MR) (5 MARKS)
C. What is the price of a bag of rice? Give a reason for your answer (5 MARKS)
D. In what market structure is the farmer operating? Explain your answer (5 MARKS)
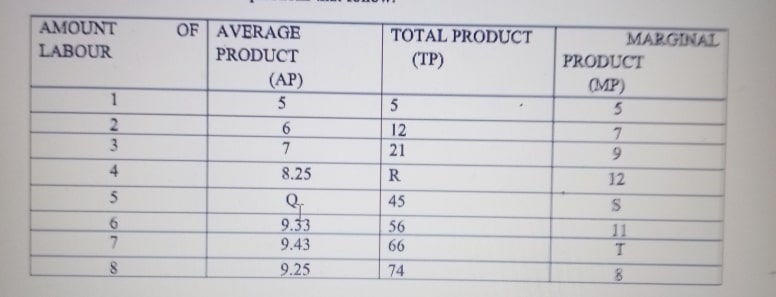
2. The table below represents the production function of a firm. Use the information to answer the questions that follow.
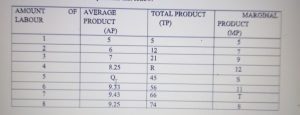
A. Calculate the values of Q,R,S and T 4 MARKS
B. Determine the levels of employment at which the firm experiences:
i. Increasing returns 2 MARKS
ii. Constant returns 2 MARKS
iii. Diminishing returns 2 MARKS
C. State the law of diminishing returns 5 MARKS
D. Mention what diminishes 2 MARKS
E. What is another name for the law of diminishing returns? 3 MARKS
SECTION C: THEORY
SDA SHS economics mock questions: Answer only three (3) questions from this section
3. a. What is production?
b. Describe each of the following sectors of economy:
i. Primary sector
ii. Secondary sector
iii. Tertiary sector
c. Highlight any three (4) contributions of the primary sector to the economic development of your country.
4. With the aid of diagram, describe a change in the supply of a commodity
a. Explain any four (4) Major causes of change in supply
b. Distinguish between change in quantity supplied and change in supply with an appropriate diagram.
SDA SHS economics mock questions
5. a. Distinguish between change in quantity supplied and change in supply with an appropriate diagram.
I. Utility
II. Marginal utility
III. Total utility
c. State any two ways in which total utility and marginal utility are related.
d. Outline the conditions of consumer equilibrium when disposable income is spent on;
i. One commodity
ii. two commodities
6. What is a market?
i. Outline any two features of monopoly Market.
ii. Describe any four features of perfect Competitive firms.
iii. Distinguish between Normal Profit and Pure (abnormal) profit.
7. a. With the aid of diagram, explain the effect of fixing price;
i. Above the equilibrium price.
ii. Below equilibrium price.
b. Explain Five (5) reasons why government controls prices.
Post Disclaimer
The information contained in this post is for general information purposes only. The information is provided by Educative News and while we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the post for any purpose.