Solution to the SHS integrated science mock questions
integrated science mock questions and answers
Solution to the SHS integrated science mock questions
Below is the solution to PARKOSO SHS integrated science mock questions. The questions are well selected to prepare candidates well towards their end school examination
Solution
1. a) (i) A fertile soil
Is a soil that contains all the necessary nutrients/minerals needed by plants
for growth/development
OR
A soil that supports plants’ healthy growth/development
OR
Ability of the soil to provide nutrients in proper quantities/in a balanced way for the growth of
plants
(ii) Conditions under which a fertile
soil will not be productive
− nutrients not able to dissolve /
nutrients not available to crops,
− type of farming method used
− unavailability of oxygen to crop roots
− lack of water / excessive drought
− crops planted too deep/beyond the rich layers of the soil
− when nutrients in the soil do not meet the needs of crops planted
− water logging
− acidity
− presence of weeds on the farm
− unsuitable temperature
− erosion
b) Description of distillation of
fermented palm wine in the laboratory
− Put the fermented palm wine in a distillation flask
− Add boiling chips to prevent bumping
− Fit a thermometer to the flask
− Connect the distillation flask to a Liebig condenser
− Clamp the distillation flask firmly and place a container under the condenser
− Heat the distillation flask,
− at 75 °C – 90 °C distillate
− the distillate is identified / tested for to be ethanol
Solution to the SHS integrated science mock questions
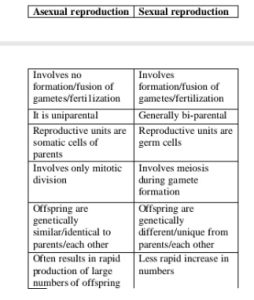
c) (i) Differences between asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction
(ii) Function of structures in the human
body
(a) alveoli- exchange of CO2 for O2 in
the lungs / gaseous exchange/diffusion of
O2 into the blood / diffusion of CO2 out of
the blood
(b) hepatic portal vein – carries
digested food /
glucose from
Small intestine
to the liver
OR
drains blood
from the
spleen to the
liver
(c) gall bladder – stores/concentrates
/releases bile into
the small intestine
d) (i) The primary colours
Red
Green
Blue
(ii) The types of equilibrium
Stable
Neutral
Unstable
Solution to the SHS integrated science mock questions
2. (a) (i) Esterification
is the reaction between alkanol and alkanoic acid to produce ester.
(ii) Observation when ethanol is
heated with ethanoic acid
A fruity/sweet smelling substance is produced.
b) Description of the use of a bar
magnet to differentiate between a
magnetic material and a bar magnet
− one end/pole of the magnet is brought close to one end of each of the test samples / bar
magnet / magnetic material
− the process is repeated using the same end of the magnet with the opposite ends of the
test samples
− there is attraction between the magnet and the magnetic material when each end of the
magnetic material is used
− there is attraction between the magnet and the bar magnet at one end and repulsion when
the other end of the bar magnet is used
Solution to the SHS integrated science mock questions
(c) Ecological factors that affect crop
production
− rainfall/water/moisture
− temperature pests and diseases
− wind
− sunshine/light
− biotic factors
− soil factors
− topography
− relative humidity
− carbon dioxide concentration
(d) (i) Explanation of the function of
the mucus lining of the respiratory
tract of humans
The mucus is a viscous fluid which help to trap dust particles /microbes
that enter the respiratory tract.
Mucus contain antibodies that recognize germs which are killed by enzymes in the fluid
OR
Mucus traps dust/germ making inhaled air harmless
(ii) Products of
(a) aerobic respiration
Water
Energy
Carbon dioxide
(b) anaerobic respiration
Lactic acid
Energy
(c) fermentation
Alcohol
Energy
Carbon dioxide
Solution to the SHS integrated science mock questions
3. (a) (i) Name of plastic for
(a) ethene – polyethene/
polyethylene /polythene
(b) chloroethene – polychloroethene/
polyvinyl chloride
(ii) Use of
(a) Polyethene/Polythene Making
bags, bottles, buckets, cups
(b) polychloroethene/polyvmyl
chloride
Making window frames, pipes, credit cards, footwear, automobile interior, cable and, wire
insulators, roofing membranes etc.
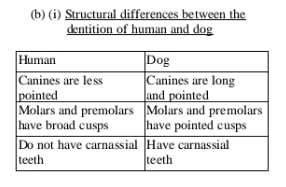
(b) (i) Structural differences between the
dentition of human and dog
(ii) Ways in which food is used by animals
− oxidized for energy / respiration
− used for growth
− for replacement of worn out cells
− for repair of damage tissue
− to keep body healthy
Solution to the SHS integrated science mock questions
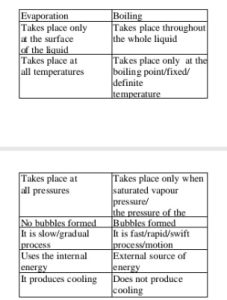
(c) (i) Differences between evaporation
and boiling
(ii) Explanation of observation water boiling at the top of test tube while the bottom, remains
cold
− water is a bad conductor of heat
− only molecules at the top get heated
− the heated molecules become
lighter and are not able to
move downward to displace
the heavier molecules
− heat is not able to be
transferred from the top to the
bottom
− hence continuous heating
causes the top to boil while
the bottom remains cold
d) (i) Distinction between hay and silage
Hay is a cut and dried forage
material meant to feed livestock in
the future.
Silage is a partially fermented
forage material preserved to feed
livestock.
(ii) Characteristics of a good laying hen
− large bright red waxy comb/wattles
− large bright/prominent/sparkling eyes
− wide soft and pliable abdomen/body fat accumulation
− oval/moist/warm vent
− usually active / alert to its surrounding / not lazy
− feathers dirty/ragged looking
bright skin/ear lobes /shanks
Solution to the SHS integrated science mock questions
4. (a) (i) Explanation of why the elements
in group I have similar chemical
properties
Chemical properties are
determined by the number of
electrons in the outermost shell
Atoms of elements in group 1 have
one electron in their outermost shells
(ii) Explanation of why noble gases are
unreactive under normal conditions
Noble gases have full complement
of electrons in their outmost shells
and therefore are very stable
(b) Propagation material for
(i) shallot – bulbs
(ii) cocoyam – corm
(iii) cassava – stem cuttings
(iv) ginger – rhizomes
(v) oil palm – seeds/nuts
Solution to the SHS integrated science mock questions
(c) (i) Structures found in plant cells
only Chloroplast, cellulose/cell
wall, starch, large/permanent
vacuoles
(ii) Functions of the mammalian skeleton
− gives the body its shape
− supports the body
− responsible for movement/attachment of
muscles
− protects the internal organs
− site for production of blood cells
d) (i) Definition of displacement
The distance moved by an
object in a specified direction
(ii) Determination of velocity of
ambulance
Conversion of 100 km to 1000 m Conversion of 2 hours to 2 x 60 x 60 s
Velocity = displacement/time
= (100 x 1000)/ (2 x 60 x 60)
= 13.9m/
Solution to the SHS integrated science mock questions
5. (a) Reasons for keeping farm records
− to know the assets of the farm
− to check mortality rate
− to compare performance of different enterprises on the farm
− to help prepare farm budget
− helps to plan ahead
− To be able to report on taxes
− Provides information for understanding activities on the farm operations
− On loan processes
− To know if inputs are eaten into your profit
− To help to educate new generation farmers
− To avoid making the same mistakes / to be able to predict the future / help to plan
improvement
− It makes it quicker to prepare account
− Help to identify the strength and weaknesses in the business
− Helps in meeting financial commitment, etc
− For reference purposes
− For breeding purposes
(b) (i) Organisms involved in the nitrogen
cycle
− Nitrogen-fixing bacteria/ Azotobacter/ Rhizobium
− Nitrosomonas
− Nitrobacter
− Nitrifying bacteria
− Denitrifying bacteria
− Lichens
(ii) Processes in the nitrogen cycle that
contribute to the return of nitrogen
to the atmosphere
− Denitrification
− Anaerobic ammonia oxidation
Solution to the SHS integrated science mock questions
(c) (i) Radioisotopes
Are unstable atoms of element which contain an
imbalance combination protons and neutrons
OR
Chemical elements that have unstable nucleus and emits radiations/
energy/particles during its decay
(to a stable form)
(ii) Problems associated withdisposal
of nuclear waste
− causes genetic problem
− exposure to nuclear waste can cause cancer/ burns
− kill fish and other living organism if released into water bodies / kills plants an
animal life
− nuclear rods remain radioactive/hazardous for long period of time / long half-life
− contamination of drinking water / air pollution
− high cost in the management of spilled radioactive material

Solution to the SHS integrated science mock questions
6. Solution

Post Disclaimer
The information contained in this post is for general information purposes only. The information is provided by Educative News and while we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the post for any purpose.